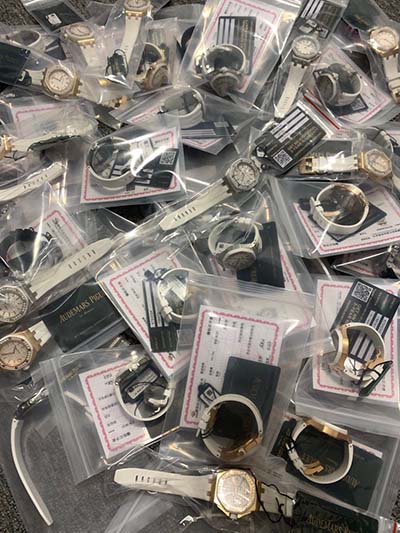
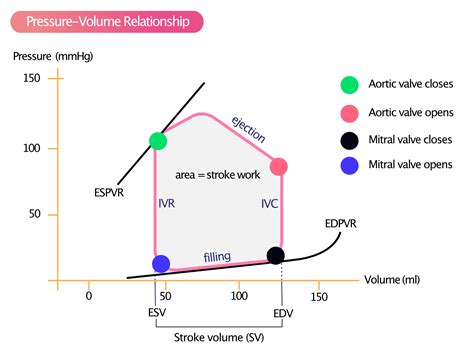
lv volume vs interventricular pressure | left ventricular pressure volume cv lv volume vs interventricular pressure Left ventricular volume decreases as the ventricle contracts and pumps blood into the aorta. After the maximum pressure is reached, the ventricle relaxes, which results in diminished left ventricular pressure. The aortic valve closes when . Buy and sell authentic used Omega Speedmaster watches. Explore great deals from local and international sellers on the Chrono24 marketplace. Financing available in the USA.
0 · ventricular volume vs lvp
1 · ventricular pressure volume relationship pdf
2 · ventricular pressure volume
3 · left ventricular pressure vs volume
4 · left ventricular pressure volume relationship
5 · left ventricular pressure volume ratio
6 · left ventricular pressure volume diagram
7 · left ventricular pressure volume cv
Le Fonds de solidarité FTQ affiche un profit de 2,9 milliards de dollars pour son exercice annuel terminé le 31 mai 2021. Le rendement annuel à l’actionnaire est de .

ventricular volume vs lvp
Left ventricular volume decreases as the ventricle contracts and pumps blood into the aorta. After the maximum pressure is reached, the ventricle relaxes, which results in diminished left ventricular pressure. The aortic valve closes when .To illustrate the pressure-volume relationship for a single cardiac cycle, the cycle can be divided into four basic phases: ventricular filling (phase a, diastole), isovolumetric contraction (phase b, systole), ejection (phase c, systole), and . Overview of pathology, histology, and magnetic resonance findings in the RV in health and disease. The pressure-overloaded RV demonstrates hypertrophy and dilatation, systolic septal flattening, and extensive fibrosis. . Pressure-volume (PV) analysis addresses these shortcomings by combining simultaneous measurements of pressure and volume to generate load-independent measures of systolic and diastolic chamber properties, and is .
In chronic pressure overload, the RV pressure-volume loop becomes less trapezoidal and squarer in shape (more “LV-like”). As a result, mean PA pressure underestimates end-systolic pressure in a degree that can be mathematically . Reducing LV volume from its optimal volume to zero caused a 5.7% decrease in RV developed pressure, whereas ligating the coronary supply to the LV free wall resulted in an additional 9.3% decrease in RV developed pressure.Right Ventricular Failure: RV is better suited to volume overload than left due to compliance and thin wall but when PVR increases for whatever reason -> RV dilates; mortality as high as LV failure.
Beat-to-beat analysis of left ventricular pressure-volume relation and stroke volume by conductance catheter and aortic Modelflow in cardiomyoplasty patients. The interventricular septum (IVS) develops out of muscular and membranous components and further endocardial tissue gives rise to the tricuspid and mitral valves (Moorman et al., 2003 ). The relative intraventricular pressure mapping of LV showed a high to low gradient from the base to apex of LV at the beginning of diastole (isovolumic relaxation period) in both .Left ventricular volume decreases as the ventricle contracts and pumps blood into the aorta. After the maximum pressure is reached, the ventricle relaxes, which results in diminished left ventricular pressure. The aortic valve closes when aortic pressure exceeds left .
To illustrate the pressure-volume relationship for a single cardiac cycle, the cycle can be divided into four basic phases: ventricular filling (phase a, diastole), isovolumetric contraction (phase b, systole), ejection (phase c, systole), and isovolumetric relaxation (phase d, diastole). Overview of pathology, histology, and magnetic resonance findings in the RV in health and disease. The pressure-overloaded RV demonstrates hypertrophy and dilatation, systolic septal flattening, and extensive fibrosis. The volume-overloaded RV demonstrates dilatation, diastolic septal flattening, and mild fibrosis. Pressure-volume (PV) analysis addresses these shortcomings by combining simultaneous measurements of pressure and volume to generate load-independent measures of systolic and diastolic chamber properties, and is considered the gold-standard method for characterizing ventricular systolic and diastolic function, as well as ventricular-vascular .
In chronic pressure overload, the RV pressure-volume loop becomes less trapezoidal and squarer in shape (more “LV-like”). As a result, mean PA pressure underestimates end-systolic pressure in a degree that can be mathematically estimated (84) . Reducing LV volume from its optimal volume to zero caused a 5.7% decrease in RV developed pressure, whereas ligating the coronary supply to the LV free wall resulted in an additional 9.3% decrease in RV developed pressure.
Right Ventricular Failure: RV is better suited to volume overload than left due to compliance and thin wall but when PVR increases for whatever reason -> RV dilates; mortality as high as LV failure.
Beat-to-beat analysis of left ventricular pressure-volume relation and stroke volume by conductance catheter and aortic Modelflow in cardiomyoplasty patients.
The interventricular septum (IVS) develops out of muscular and membranous components and further endocardial tissue gives rise to the tricuspid and mitral valves (Moorman et al., 2003 ).
The relative intraventricular pressure mapping of LV showed a high to low gradient from the base to apex of LV at the beginning of diastole (isovolumic relaxation period) in both patients (B, E).Left ventricular volume decreases as the ventricle contracts and pumps blood into the aorta. After the maximum pressure is reached, the ventricle relaxes, which results in diminished left ventricular pressure. The aortic valve closes when aortic pressure exceeds left .To illustrate the pressure-volume relationship for a single cardiac cycle, the cycle can be divided into four basic phases: ventricular filling (phase a, diastole), isovolumetric contraction (phase b, systole), ejection (phase c, systole), and isovolumetric relaxation (phase d, diastole). Overview of pathology, histology, and magnetic resonance findings in the RV in health and disease. The pressure-overloaded RV demonstrates hypertrophy and dilatation, systolic septal flattening, and extensive fibrosis. The volume-overloaded RV demonstrates dilatation, diastolic septal flattening, and mild fibrosis.
Pressure-volume (PV) analysis addresses these shortcomings by combining simultaneous measurements of pressure and volume to generate load-independent measures of systolic and diastolic chamber properties, and is considered the gold-standard method for characterizing ventricular systolic and diastolic function, as well as ventricular-vascular .
ventricular pressure volume relationship pdf
In chronic pressure overload, the RV pressure-volume loop becomes less trapezoidal and squarer in shape (more “LV-like”). As a result, mean PA pressure underestimates end-systolic pressure in a degree that can be mathematically estimated (84) . Reducing LV volume from its optimal volume to zero caused a 5.7% decrease in RV developed pressure, whereas ligating the coronary supply to the LV free wall resulted in an additional 9.3% decrease in RV developed pressure.
Right Ventricular Failure: RV is better suited to volume overload than left due to compliance and thin wall but when PVR increases for whatever reason -> RV dilates; mortality as high as LV failure. Beat-to-beat analysis of left ventricular pressure-volume relation and stroke volume by conductance catheter and aortic Modelflow in cardiomyoplasty patients. The interventricular septum (IVS) develops out of muscular and membranous components and further endocardial tissue gives rise to the tricuspid and mitral valves (Moorman et al., 2003 ).

ysl red box
Born out of a collab between Le Specs x Adam Selman, the iconic slim black cat eye sunglasses are the most flattering and chic pair of sunglasses I’ve ever owned, dating back to my days.
lv volume vs interventricular pressure|left ventricular pressure volume cv